Talk:Huperzine A
This page has not been fully approved by the PsychonautWiki administrators. It may contain incorrect information, particularly with respect to dosage, duration, subjective effects, toxicity and other risks. It may also not meet PW style and grammar standards. |
| Summary sheet: Huperzine A |
| Huperzine A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Nomenclature | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common names | Huperzine A、HupA | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substitutive name | Huperzine A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systematic name | 5,9-Methanocycloocta[b]pyridin-2(1H)-one, 5-amino-11-ethylidene-5,6,9,10-tetrahydro-7-methyl-, (5R,9R,11E)- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class Membership | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Psychoactive class | Nootropic / Oneirogen | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical class | Others | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Routes of Administration | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
For tips on how to properly format a substance article, please refer to this document: Content Style Guide - Substance
Huperzine A is a drug used to treat alzheimers and schizophrenia induced cognitive impairment. It is also used as a nootropic. It is a natural compound that occurs in multiple plants in the genus Huperzia and was first isolated and pharmacologically characterized by Chinese scientists in 1986 [3].
History and culture
This History and culture section is a stub. As a result, it may contain incomplete or wrong information. You can help by expanding it. |
Since initial discovery, scientists have been interested in huperzine A due to its pharmacological profile and potential anti-neurodegenerative properties [4]. Huperzine A has indeed been shown to indirectly influence several signaling pathways associated with neuroprotection, including neurotrophic factors or Wnt, and decreased amyloid beta accumulation in vivo.[5]. Besides its popularity in biomedical research, huperzine A is also commonly sold as a supplement for its ability to improve cognitive function. However, some placebo controled studies indicate low efficiancy [6].
Among psychonauts, huperzine A has also found its popularity as a dream potentiator and inducer of lucid dreams, similar to the less available galantamine [7]
Chemistry
This chemistry section is incomplete. You can help by adding to it. |
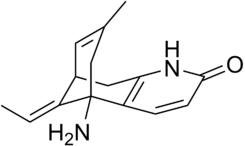
Huperzine A is a polycyclic sesquiterpene alkaloid with molecular formula of C15H18N2O [8]. Its biosynthesis is not well researched and likely involves both precursors of isoprenoids and alkaloids [9]. Multiple total syntheses have also been performed [10].
Pharmacology
This pharmacology section is incomplete. You can help by adding to it. |
Huperzine A is a reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and NMDA receptor antagonist.
Subjective effects
| This subjective effects section is a stub. As such, it is still in progress and may contain incomplete or wrong information. You can help by expanding or correcting it. |
Disclaimer: The effects listed below cite the Subjective Effect Index (SEI), an open research literature based on anecdotal user reports and the personal analyses of PsychonautWiki contributors. As a result, they should be viewed with a healthy degree of skepticism.
It is also worth noting that these effects will not necessarily occur in a predictable or reliable manner, although higher doses are more liable to induce the full spectrum of effects. Likewise, adverse effects become increasingly likely with higher doses and may include addiction, severe injury, or death ☠.
Physical effects
- If applicable, a brief paragraph summary of the substance's physical effects may be included here. You may select physical effects to add below here.
Visual effects
-
If applicable, a brief paragraph summary of the substance's visual effects may be included here.
You may select visual effects to add below here.
Enhancements
Distortions
- Visual acuity supression - Typically at higher doses, huperzine a can cause blurred vision. This is likely due to its activity as an NMDA antagonist.
'
Cognitive effects
-
If applicable, a brief paragraph summary of the substance's cognitive effects may be included here.
You may select from a list of cognitive effects to add below here.
- Cognitive euphoria
- Thought acceleration
- Thought organization
- Creativity enhancement
- Anxiety suppression
- Increased music appreciation
- Wakefulness
- Mindfulness
- Focus enhancement
- Analysis enhancement
- Time distortion
- Memory enhancement
- Irritability
- Increased libido
- Motivation enhancement
- Dream potentiation
- Increased sense of humor
- Emotion enhancement
Experience reports
There are currently no anecdotal reports which describe the effects of this compound within our experience index. Additional experience reports can be found here:
Toxicity and harm potential
This toxicity and harm potential section is a stub. As a result, it may contain incomplete or even dangerously wrong information! You can help by expanding upon or correcting it. |
It is strongly recommended that one use harm reduction practices when using this substance.
Lethal dosage
The exact lethal dosage of Huperzine A in humans is not well-documented. However, it is known to have a wide margin of safety and is generally considered non-toxic even at doses 50-100 times the therapeutic dose.[11]
Tolerance and addiction potential
Huperzine A is not known to be not habit-forming and the desire to use it can actually decrease with use. It is most often self-regulating.
Huperzine A does not seem to build up an immediate tolerance, and, due to its long half life (10-14 hours), becomes stronger with prolonged use. Caution should be taken when using Huperzine A for extended periods longer than two weeks. Huperzine A presents cross-tolerance with no other known compounds, meaning that after the consumption of Huperzine A all other psychoactive compounds will not have a reduced effect.
Dangerous interactions
This dangerous interactions section is a stub. As such, it may contain incomplete or invalid information. You can help by expanding upon or correcting it. |
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors - Huperzine A may result in a cholinergic crisis when combined with other potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Caution should also be exercised when combining Huperzine
A with caffeine or nicotine.
- Dissociatives - Huperzine A has an antagonistic effect on NMDA receptors and may enhance the dissociative effects of these dissociative agentsWarning: Many psychoactive substances that are reasonably safe to use on their own can suddenly become dangerous and even life-threatening when combined with certain other substances. The following list provides some known dangerous interactions (although it is not guaranteed to include all of them).
Always conduct independent research (e.g. Google, DuckDuckGo, PubMed) to ensure that a combination of two or more substances is safe to consume. Some of the listed interactions have been sourced from TripSit.
Potentiation of dissociatives
Due to the ability of Huperzine A to antagonize NMDA receptors, it may potentiate the effects of dissociative compounds such as DXM, MXE, or Ketamine.
Legal status
This legality section is a stub. As such, it may contain incomplete or wrong information. You can help by expanding it. |
See also
External links
Literature
- APA formatted reference
Please see the citation formatting guide if you need assistance properly formatting citations.
References
- ↑ 石杉碱甲胶囊说明书
- ↑ 链接文本,附加文本。
- ↑ Wang YE, Yue DX, Tang XC. [Anti-cholinesterase activity of huperzine A]. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1986 Mar;7(2):110-3. Chinese. PMID: 2946143.
- ↑ Yang G, Wang Y, Tian J, Liu JP. Huperzine A for Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. PLoS One. 2013 Sep 23;8(9):e74916. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074916. PMID: 24086396; PMCID: PMC3781107.
- ↑ Friedli MJ, Inestrosa NC. Huperzine A and Its Neuroprotective Molecular Signaling in Alzheimer's Disease. Molecules. 2021 Oct 29;26(21):6531. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216531. PMID: 34770940; PMCID: PMC8587556.
- ↑ Wessinger CM, Inman CL, Weinstock J, Weiss EP. Effect of Huperzine A on Cognitive Function and Perception of Effort during Exercise: A Randomized Double-Blind Crossover Trial. Int J Exerc Sci. 2021 Aug 1;14(2):727-741. PMID: 34567353; PMCID: PMC8439683.
- ↑ https://www.world-of-lucid-dreaming.com/lucid-dream-pills.html
- ↑ National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 854026, Huperzine A. Retrieved November 21, 2023 from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/854026.
- ↑ Li X, Li W, Tian P, Tan T. Delineating biosynthesis of Huperzine A, A plant-derived medicine for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Biotechnol Adv. 2022 Nov;60:108026. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2022.108026. Epub 2022 Jul 30. PMID: 35914626.
- ↑ Total Synthesis of (−)-Huperzine A Takahiro Koshiba, Satoshi Yokoshima, and Tohru Fukuyama Organic Letters 2009 11 (22), 5354-5356 DOI: 10.1021/ol9022408
- ↑ Review of the value of huperzine as pretreatment of organophosphate poisoning,Review of the value of huperzine as pretreatment of organophosphate poisoning.